VHDL code for UART (Serial Communication)
UART Stands for Universal Asynchronous Transmitter Receiver. The function of UART is conversion parallel data (8 bit) to serial data. UART transmit bytes of data sequentially one bit at a time from source and receive the byte of data at the destination by decoding sequential data with control bits. As the entire processes require no clock input from source hence it is termed as asynchronous communication.
Baud Rate
In the UART communication data transmission speed is measured by Baud Rate. Baud rate describes the total number of bit sent through serial communication. It includes Start bit, Data byte, Parity bit and Stop bit. Transmitter and receiver need to be maintained in the baud rate. For example Spartan3 FPGA Image Processing Boardtransmit data at the baud rate of 9600 and at the receiving end PC need to be set with same baud rate using HyperTerminal or TeraTerminal.
Packet of Data in Serial Communication
Serial Communication consist of 2 lines Transmitter and Receiver pin.
Fig 1:Connection between FPGA and PC
Serial data communicate on FPGA side range in 0 to 3.3v. Logic 0 is represented by 0v. Logic 1 is represented by 3.3v
Fig 2: Voltage level of FPGA
On PC Side RS232 Port voltage range from -15v to +15v. Logic 0 is represented by +3v to 15v. Logic 1 is represented by -3v to -15v
Fig 3: Voltage level of PC
In order to communicate between FPGA and PC with different voltage level, MAX3232 Driver IC is required. It consists of 2 channel transmitter and Receiver.
Serial communication
The data communication of UART is made by 11 bit blocks.
Fig 4: Serial communication
The wave form showed the protocol of the UART. Here the ‘0’ bit represent as start bit which is initiated the serial communication. The start bit must be ‘0’. The next 8 bit’s are data bit. The LSB bit of data goes as first bit continue it sent other 7 bits. The 10th bit is a parity bit which is used to identify error in the communication. The parity bit is either 0 or 1 which is depending on the number of 1’s present in transmission. If even parity is used, the number of bit must be even. If odd parity is used, the number of bit must be odd. The speed of transmission is fixed which is measured by baud rate. The last bit is stop bit which must be ‘1’.
Note: The parity bit is not necessary which is optional.
Transmission delay
The transmission rate is measured by bits per second. Each bit has a fixed time duration while transmission. The transmission delay for each bit 104.16 μs which is constant till the end of communication.
Example
The baud rate is 9600.
Transmission delay =1/9600 =104.16 μs.
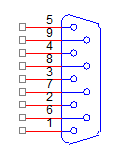
RS 232 connector and cable
RS 232 connector is used to establish connection between Spartan3 FPGA Image Processing Board and PC. It is either male or female connector. Here we use only female to female connector. RS 232 connector has only 9 pins, even though the only 3 pins are enough to make a transmission between PC and FPGA such as RD,TD and GND.
Fig 5:RS232 connector
Table 1:
| Pin no | Signal |
| 1 | Data carrier detect(DCD) |
| 2 | DReceived data(RD) |
| 3 | Transmitted data(TD) |
| 4 | Data terminal ready(DTR) |
| 5 | Signal ground(GND) |
| 6 | Data set ready(DSR) |
| 7 | Request to send(RS) |
| 7 | Clear to send(CS) |
| 8 | Ring indicator(RI) |
RS232 interface using Max3232 Driver IC with Spartan3 FPGA Image Processing Board
Fig 6: Schematic diagram of FPGA and MAX 3232
UART Placement in Spartan3 FPGA Image Processing Board
In this article, 3 example codes are provided to demonstrate the UART Communication.
1st VHDL Code describes Transmitting data from PC HyperTerminal to Spartan3 FPGA Image Processing Board and feedback to PC at 9600 Baud Rate.
This Code consists of Clock and Reset input. Clock running at 50MHz and Reset is assigned to Slide switch to enable or disable Serial Communication. Din and Do are transmit and receive of the FPGA. The Functionality of this code can be explained by 2 process statements. Process 1 involves transmission of data from PC to FPGA and stores them in array. Process 2 involves retransmission of data stores in FPGA array to PC.
VHDL Code for Serial Communication Transmitting data from PC to Spartan3 FPGA Image Processing Board and feedback to PC at 9600 Baud Rate
library IEEE;
use IEEE.STD_LOGIC_1164.ALL;
use IEEE.STD_LOGIC_ARITH.ALL;
use IEEE.STD_LOGIC_UNSIGNED.ALL;
entity uart is
port ( clk : in std_logic; -----system clock i/p
reset : in std_logic; -----switch input
din : in std_logic; -----fpga receive i/p
do : out std_logic); ------fpga transmit o/p
end uart;
architecture Behavioral of uart is
type state is (ready,b0,b1,b2,b3,b4,b5,b6,b7,b8); ----fsm for receive
signal ps : state := ready;
type state1 is (ready1,b01,b11,b21,b31,b41,b51,b61,b71,b81); -----fsm for transmit
signal ps1 : state1 := ready1;
signal start,stop : std_logic := '0';
signal store : std_logic_vector(7 downto 0) := "00000000"; ----storing of recived value
begin
process(reset,clk)
variable i : integer := 0 ;
begin
if reset = '1' then
if clk'event and clk = '1' then
if ps = ready then ----logic to detect the transmission start
start <= din;
end if;
if start = '0' then
ps <= b0;
elsif start = '1' then
ps <= ready;
end if;
------------------------------------------1
if ps = b0 then
store(0) <= din; -----receive and store of each bit
i := i + 1;
ps <= b0;
if i = 5209 then -----timing delay to receive bit
i := 0;
ps <= b1;
end if;
end if;
------------------------------------------2
if ps = b1 then
store(1) <= din;
i := i + 1;
ps <= b1;
if i = 5209 then
i := 0;
ps <= b2;
end if;
end if;
-----------------------------------------3
if ps = b2 then
store(2) <= din;
i := i + 1;
ps <= b2;
if i = 5209 then
i := 0;
ps <= b3;
end if;
end if;
----------------------------------------4
if ps = b3 then
store(3) <= din;
i := i + 1;
ps <= b3;
if i = 5209 then
i := 0;
ps <= b4;
end if;
end if;
---------------------------------------5
if ps = b4 then
store(4) <= din;
i := i + 1;
ps <= b4;
if i = 5209 then
i := 0;
ps <= b5;
end if;
end if;
---------------------------------------6
if ps = b5 then
store(5) <= din;
i := i + 1;
ps <= b5;
if i = 5209 then
i := 0;
ps <= b6;
end if;
end if;
---------------------------------------7
if ps = b6 then
store(6) <= din;
i := i + 1;
ps <= b6;
if i = 5209 then
i := 0;
ps <= b7;
end if;
end if;
--------------------------------------8
if ps = b7 then
store(7) <= din;
i := i + 1;
ps <= b7;
if i = 5209 then
i := 0;
ps <= b8;
end if;
end if;
--------------------------------------9
if ps = b8 then
stop <= din;
i := i + 1;
ps <= b8;
if i = 5209 then
i := 0;
ps <= ready;
end if;
end if;
-------------------------------------10
end if;
end if;
end process;
----------------------------------------------------------------------transmit
process(reset,clk)
variable i : integer := 0 ;
begin
if reset = '1' then
if clk'event and clk = '1' then
if ps1 = ready1 then
if start = '0' then -----logic to indicate the communication to the partner
do <= '0';
i := i + 1;
ps1 <= ready1;
if i = 5209 then
i := 0;
ps1 <= b01;
end if;
elsif start = '1' then
ps1 <= ready1;
end if;
end if;
------------------------------------------1
if ps1 = b01 then
do <= store(0); ----transmission of each bit
i := i + 1;
ps1 <= b01;
if i = 5209 then ----timing delay for transmission of each bit
i := 0;
ps1 <= b11;
end if;
end if;
------------------------------------------2
if ps1 = b11 then
do <= store(1);
i := i + 1;
ps1 <= b11;
if i = 5209 then
i := 0;
ps1 <= b21;
end if;
end if;
-----------------------------------------3
if ps1 = b21 then
do <= store(2);
i := i + 1;
ps1 <= b21;
if i = 5209 then
i := 0;
ps1 <= b31;
end if;
end if;
----------------------------------------4
if ps1 = b31 then
do <= store(3);
i := i + 1;
ps1 <= b31;
if i = 5209 then
i := 0;
ps1 <= b41;
end if;
end if;
---------------------------------------5
if ps1 = b41 then
do <= store(4);
i := i + 1;
ps1 <= b41;
if i = 5209 then
i := 0;
ps1 <= b51;
end if;
end if;
---------------------------------------6
if ps1 = b51 then
do <= store(5);
i := i + 1;
ps1 <= b51;
if i = 5209 then
i := 0;
ps1 <= b61;
end if;
end if;
---------------------------------------7
if ps1 = b61 then
do <= store(6);
i := i + 1;
ps1 <= b61;
if i = 5209 then
i := 0;
ps1 <= b71;
end if;
end if;
--------------------------------------8
if ps1 = b71 then
do <= store(7);
i := i + 1;
ps1 <= b71;
if i = 5209 then
i := 0;
ps1 <= b81;
end if;
end if;
--------------------------------------9
if ps1 = b81 then
do <= '1';
i := i + 1;
ps1 <= b81;
if i = 5209 then
i := 0;
ps1 <= ready1;
end if;
end if;
-------------------------------------10
end if;
end if;
end process;
end Behavioral;
NET "clk" LOC = "p55" ; NET "din" LOC = "p60" ; NET "do" LOC = "p63" ; NET "reset" LOC = "p99" ;
2nd VHDL Code simply describes transmitting data from Spartan3 FPGA Image Processing Board to PC.
This Code consists of Clock input and Transmitter output from Spartan3 FPGA Image Processing Board Clock running at 50MHz. The VHDL Code for UART simply transmits data stored in the FPGA to PC. The Clock frequency can be easily modified using the parameter system_speed. Also Baud rate can be changed by modifying the parameter clock_out_speed.
VHDL Code for transmitting data from FPGA to PC
library IEEE; use IEEE.STD_LOGIC_1164.ALL; use IEEE.NUMERIC_STD.ALL; entity uart_transmitter is port( clock: in std_logic; txd: out std_logic); end uart_transmitter; architecture Behavioral of uart_transmitter is constant system_speed: natural := 50e6; signal baudrate_clock, second_clock, old_second_clock: std_logic; signal bit_counter: unsigned(3 downto 0) := x"9"; signal shift_register: unsigned(9 downto 0) := (others => '0'); signal char_index: natural range 0 to 18; component clock_generator generic(clock_in_speed, clock_out_speed: integer); port( clock_in: in std_logic; clock_out: out std_logic); end component; begin baudrate_generator: clock_generator generic map(clock_in_speed => system_speed, clock_out_speed => 9600) port map( clock_in => clock, clock_out => baudrate_clock); second_generator: clock_generator generic map(clock_in_speed => system_speed, clock_out_speed => 1) port map( clock_in => clock, clock_out => second_clock); send: process(baudrate_clock) begin if baudrate_clock'event and baudrate_clock = '1' then txd <= '1'; if bit_counter = 9 then if second_clock /= old_second_clock then old_second_clock <= second_clock; if second_clock = '1' then bit_counter <= x"0"; char_index <= char_index + 1; case char_index is when 0 => shift_register <= b"1" & x"50" & b"0";---P when 1 => shift_register <= b"1" & x"41" & b"0";---A when 2 => shift_register <= b"1" & x"4E" & b"0";---N when 3 => shift_register <= b"1" & x"54" & b"0";---T when 4 => shift_register <= b"1" & x"45" & b"0";---E when 5 => shift_register <= b"1" & x"43" & b"0";---C when 6 => shift_register <= b"1" & x"48" & b"0";---H when 7 => shift_register <= b"1" & x"20" & b"0"; when 8 => shift_register <= b"1" & x"53" & b"0";---S when 9 => shift_register <= b"1" & x"4F" & b"0";---O when 10 => shift_register <= b"1" & x"4C" & b"0";---L when 11 => shift_register <= b"1" & x"55" & b"0";---U when 12 => shift_register <= b"1" & x"54" & b"0";---T when 13 => shift_register <= b"1" & x"49" & b"0";---I when 14 => shift_register <= b"1" & x"4F" & b"0";---O when 15 => shift_register <= b"1" & x"4E" & b"0";---N when 16 => shift_register <= b"1" & x"53" & b"0";---S when 17 => shift_register <= b"1" & x"20" & b"0";---SPACE BAR when 18 => shift_register <= b"1" & x"20" & b"0";--- SPACE BAR char_index <= 0; when others => char_index <= 0; end case; end if; end if; else txd <= shift_register(0); bit_counter <= bit_counter + 1; shift_register <= shift_register ror 1; end if; end if; end process; end Behavioral;
library IEEE; use IEEE.STD_LOGIC_1164.ALL; use IEEE.NUMERIC_STD.ALL; entity clock_generator is generic(clock_in_speed, clock_out_speed: integer); port( clock_in: in std_logic; clock_out: out std_logic); end entity clock_generator; architecture Behavioral of clock_generator is function num_bits(n: natural) return natural is begin if n > 0 then return 1 + num_bits(n / 2); else return 1; end if; end num_bits; constant max_counter: natural := clock_in_speed / clock_out_speed / 2; constant counter_bits: natural := num_bits(max_counter); signal counter: unsigned(counter_bits - 1 downto 0) := (others => '0'); signal clock_signal: std_logic; begin update_counter: process(clock_in) begin if clock_in'event and clock_in = '1' then if counter = max_counter then counter <= to_unsigned(0, counter_bits); clock_signal <= not clock_signal; else counter <= counter + 1; end if; end if; end process; clock_out <= clock_signal; end Behavioral;
User Constraint File
NET "clock" LOC = P55; NET "txd" LOC = P63;
3rd VHDL Code describes Controlling On/Off Spartan3 FPGA Image Processing Board interfaced devices such as Relay, Buzzer, LED etc from PC HyperTerminal.
This Code consists of Clock input and Receive input to Spartan3 FPGA Image Processing Boardand 2 LED output. Clock running at 50MHz. The VHDL Code for UART receives data from PC and ON/OFF LED’s in the FPGA.
VHDL Code for Controlling LED’s interfaced Spartan3 FPGA Image Processing Board from PC HyperTerminal
library IEEE; use IEEE.STD_LOGIC_1164.ALL; use IEEE.STD_LOGIC_ARITH.ALL; use IEEE.STD_LOGIC_UNSIGNED.ALL; entity uart_reciever is port ( clk : in std_logic; din : in std_logic; led1 : out std_logic; led2 : out std_logic); end uart_reciever; architecture Behavioral of uart_reciever is type state is (ready,b0); signal ps : state := ready; type state1 is (st1,st2); signal ps1 : state1 := st1; signal start,stop : std_logic; signal store : std_logic_vector(7 downto 0) := "10101010"; begin process(clk) variable i : integer := 0 ; begin if clk'event and clk = '1' then if ps = ready then start <= din; end if; if start = '0' then ps <= b0; elsif start = '1' then ps <= ready; end if; ------------------------------------------1 if ps = b0 then i := i + 1; if i = 2600 then start <= din; end if; if i = 7800 then store(0) <= din; end if; if i = 13000 then store(1) <= din; end if; if i = 18200 then store(2) <= din; end if; if i = 23400 then store(3) <= din; end if; if i = 28600 then store(4) <= din; end if; if i = 33800 then store(5) <= din; end if; if i = 39000 then store(6) <= din; end if; if i = 44200 then store(7) <= din; end if; if i = 49400 then stop <= din; end if; if i = 54600 then i := 0 ; ps <= ready ; -----------------------------------------------------10 end if; end if; end if; end process; process(clk,store) begin if clk'event and clk = '1' then if ps1 = st1 then if store = x"31" then led1 <= '1' ; ps1 <= st2 ; elsif store = x"32" then led1 <= '0' ; ps1 <= st2 ; else ps1 <= st2 ; null; end if; end if; if ps1 = st2 then if store = x"33" then led2 <= '1' ; ps1 <= st1 ; elsif store = x"34" then led2 <= '0' ; ps1 <= st1 ; else ps1 <= st1 ; null; end if; end if; end if; end process; end Behavioral
User Constraint File
NET "clk" LOC = P55; NET "din" LOC = P60; NET "l1" LOC = P82; NET "l2" LOC = P83;