Fake News Detection using Machine Learning
₹7,500.00 Exc Tax
Fake News Detection using Machine Learning
Platform : Python
Delivery Duration : 3-4 working Days
99 in stock
Description
ABSTRACT
This Project comes up with the applications of NLP (Natural Language Processing) techniques for detecting the ‘fake news’, that is, misleading news stories that comes from the non-reputable sources. Only by building a model based on a count vectorizer (using word tallies) or a (Term Frequency Inverse Document Frequency) tfidf matrix, (word tallies relative to how often they’re used in other articles in your dataset) can only get you so far. But these models do not consider the important qualities like word ordering and context. It is very possible that two articles that are similar in their word count will be completely different in their meaning. The data science community has responded by taking actions against the problem. There is a Kaggle competition called as the “Fake News Challenge” and Facebook is employing AI to filter fake news stories out of users’ feeds. Combatting the fake news is a classic text classification project with a straight forward proposition. Is it possible for you to build a model that can differentiate between “Real “news and “Fake” news? So a proposed work on assembling a dataset of both fake and real news and employ a Naive Bayes classifier in order to create a model to classify an article into fake or real based on its words and phrases.
DEMO VIDEO
OBJECTIVE
The main objective is to detect the fake news, which is a classic text classification problem with a straight forward proposition. It is needed to build a model that can differentiate between “Real” news and “Fake” news
INTRODUCTION
These days’ fake news is creating different issues from sarcastic articles to a fabricated news and plan government propaganda in some outlets. Fake news and lack of trust in the media are growing problems with huge ramifications in our society. Obviously, a purposely misleading story is “fake news “ but lately blathering social media’s discourse is changing its definition. Some of them now use the term to dismiss the facts counter to their preferred viewpoints.
The importance of disinformation within American political discourse was the subject of weighty attention , particularly following the American president election . The term ‘fake news’ became common parlance for the issue, particularly to describe factually incorrect and misleading articles published mostly for the purpose of making money through page views. In this paper,it is seeked to produce a model that can accurately predict the likelihood that a given article is fake news.
Facebook has been at the epicenter of much critique following media attention. They have already implemented a feature to flag fake news on the site when a user sees’s it ; they have also said publicly they are working on to to distinguish these articles in an automated way. Certainly, it is not an easy task. A given algorithm must be politically unbiased – since fake news exists on both ends of the spectrum – and also give equal balance to legitimate news sources on either end of the spectrum. In addition, the question of legitimacy is a difficult one.However, in order to solve this problem, it is necessary to have an understanding on what Fake News is. Later, it is needed to look into how the techniques in the fields of machine learning, natural language processing help us to detect fake news.
EXISTING SYSTEM
There exists a large body of research on the topic of machine learning methods for deception detection, most of it has been focusing on classifying online reviews and publicly available social media posts. Particularly since late 2016 during the American Presidential election, the question of determining ‘fake news’ has also been the subject of particular attention within the literature.
Conroy, Rubin, and Chen [1] outlines several approaches that seem promising towards the aim of perfectly classify the misleading articles. They note that simple content-related n-grams and shallow parts-of-speech (POS) tagging have proven insufficient for the classification task, often failing to account for important context information. Rather, these methods have been shown useful only in tandem with more complex methods of analysis. Deep Syntax analysis using Probabilistic Context Free Grammars (PCFG) have been shown to be particularly valuable in combination with n-gram methods. Feng, Banerjee, and Choi [2] are able to achieve 85%-91% accuracy in deception related classification tasks using online review corpora.
Feng and Hirst implemented a semantic analysis looking at ‘object:descriptor’ pairs for contradictions with the text on top of Feng’s initial deep syntax model for additional improvement. Rubin, Lukoianova and Tatiana analyze rhetorical structure using a vector space model with similar success. Ciampaglia et al. employ language pattern similarity networks requiring a pre-existing knowledge base.
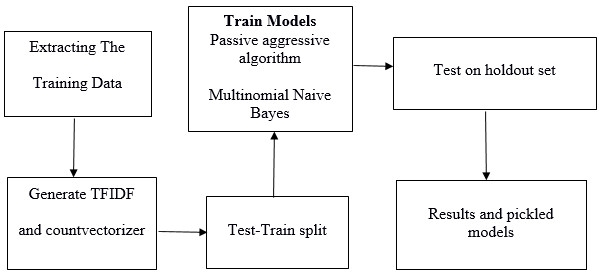
PROPOSED SYSTEM
In this paper a model is build based on the count vectorizer or a tfidf matrix ( i.e ) word tallies relatives to how often they are used in other artices in your dataset ) can help . Since this problem is a kind of text classification, Implementing a Naive Bayes classifier will be best as this is standard for text-based processing. The actual goal is in developing a model which was the text transformation (count vectorizer vs tfidf vectorizer) and choosing which type of text to use (headlines vs full text). Now the next step is to extract the most optimal features for countvectorizer or tfidf-vectorizer, this is done by using a n-number of the most used words, and/or phrases, lower casing or not, mainly removing the stop words which are common words such as “the”, “when”, and “there” and only using those words that appear at least a given number of times in a given text dataset.
COLLECTING DATA
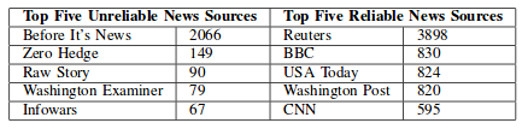
So, there must be two parts to the data-acquisition process, “fake news” and “real news”. Collecting the fake news was easy as Kaggle released a fake news dataset consisting of 13,000 articles published during the 2016 election cycle. Now the later part is very difficult. That is to get the real news for the fake news dataset. It requires huge work around many Sites because it was the only way to do web scraping thousands of articles from numerous websites. With the help of web scraping a total of 5279 articles, real news dataset was generated, mostly from media organizations (New York Times, WSJ, Bloomberg, NPR, and the Guardian) which were published around 2015 – 2016.
REQUIREMENTS
- Python
- numpy
- pandas
- itertools
- matplotlib
- sklearn
RESULTS
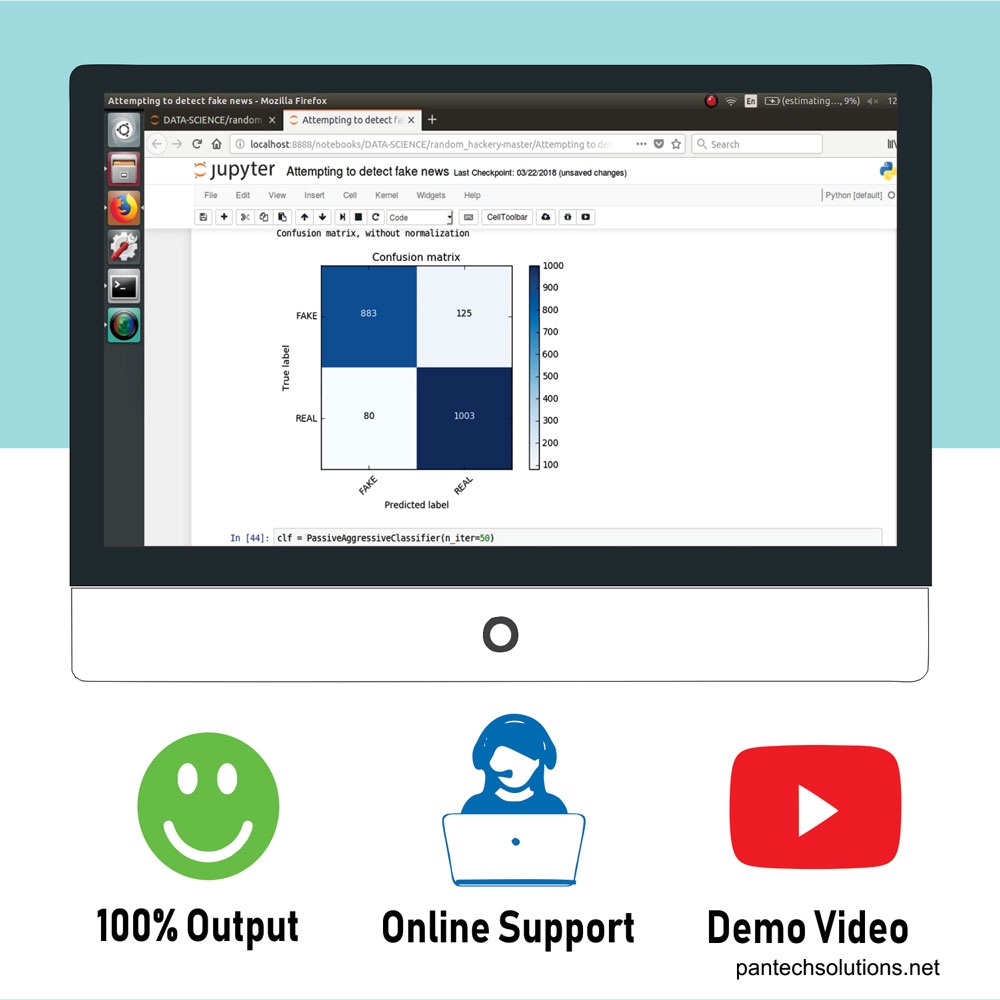
For testing the performance the Sci-kit Learn’s GridSearch functionality is utilized to efficiently execute this task.The optimal parameters for count vectorizer are no lowercasing, two-word phrases not single words, and to only use words that appear at least three times in the corpus.
This model’s cross-validated accuracy score is 91.7%, true positive score is 92.6%, and its AUC score is 95%.
REFERENCES
1) N. J. Conroy, V. L. Rubin, and Y. Chen, “Automatic deception detection: Methods for finding fake news,” Proceedings of the Association for Information Science and Technology, vol. 52, no. 1, pp. 1–4, 2015.
2) S. Feng, R. Banerjee, and Y. Choi, “Syntactic stylometry for deception detection,” in Proceedings of the 50th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Short Papers-Volume 2, Association for Computational Linguistics, 2012, pp. 171–175.
3)Shlok Gilda,Department of Computer Engineering, Evaluating Machine Learning Algorithms for Fake News Detection,2017 IEEE 15th Student Conference on Research and Development (SCOReD)


Reviews
There are no reviews yet.