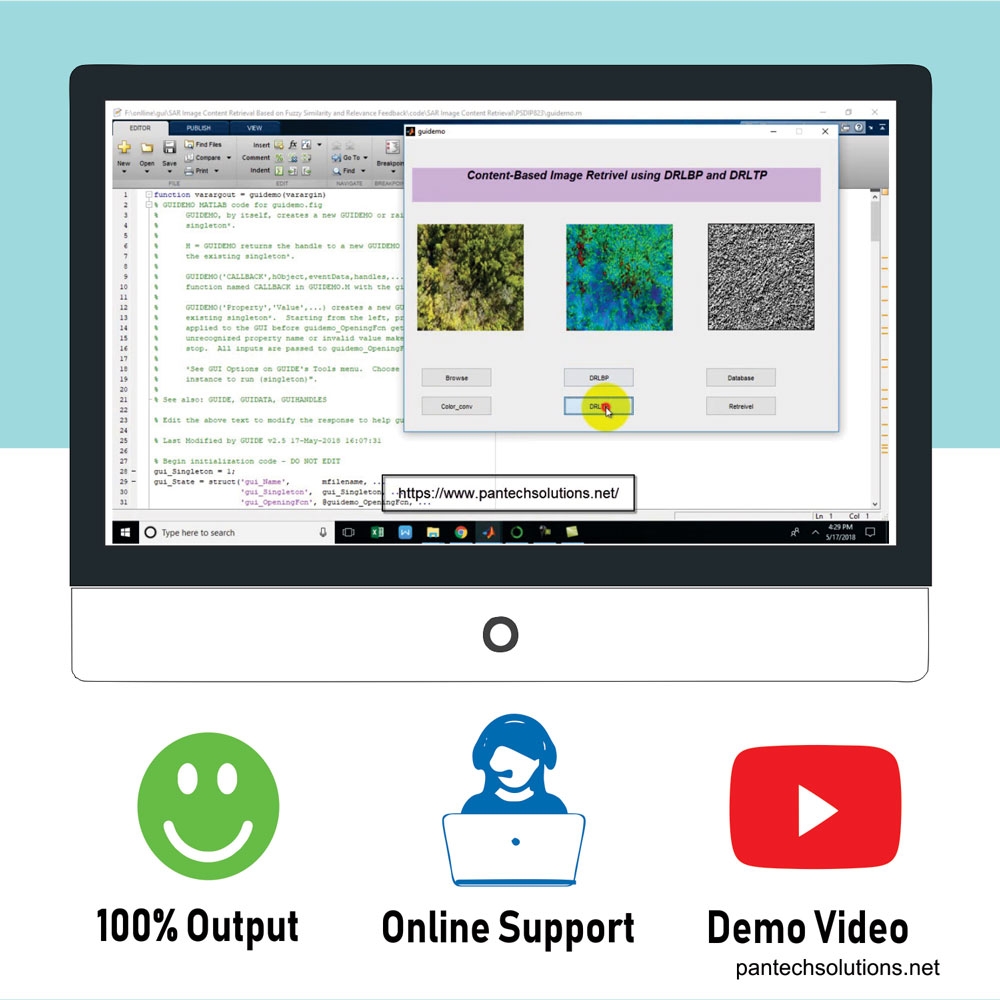
Content Based Image Retrieval using DRLBP
₹3,000.00
Huge Price Drop : 50% Discount
Source Code + Demo Video
100 in stock
Description
ABSTRACT
Content-based histology image retrieval systems have shown great potential in supporting decision making in clinical activities, teaching, and biological research. In content-based image retrieval, feature combination plays a key role. It aims at enhancing the descriptive power of visual features corresponding to semantically meaningful queries. The images format in the database is RGB format and due to colour changes of the image affected by illumination especially for outdoor image acquisition, so RGB model gives different values in different environment that may reduce the retrieval performance but HSV model gives more stability to that affect since the colour information of HSV space is distributed separately from the illumination part in different channels. The performance of the image retrieval is differentiated by different wavelet transforms because they provide the image information more effectively and GLCM is an old and classic method used to describe the texture in variety of image recognition fields. GLCM is useful since it can contain three major elements, texture information, histogram information and edge information. GLCM provides the rules that gray scale of a pair of pixels appears in a certain distance away in a certain direction. Finally, a practical results show the better retrieval performance based on wavelet, K-means cluster and GLCM features. Herein, we propose the definition of feature vectors using the Local Binary Pattern (LBP) operator. A study was performed in order to determine the optimum LBP variant for the general definition of image feature vectors. The chosen LBP variant is then subsequently used to build an ultrasound image database, and a database with images obtained from Wireless Capsule Endoscopy. The image indexing process is optimized using data clustering techniques for images belonging to the same class. Finally, the proposed indexing method is compared to the classical indexing Technique, which is nowadays widely used.
INTRODUCTION
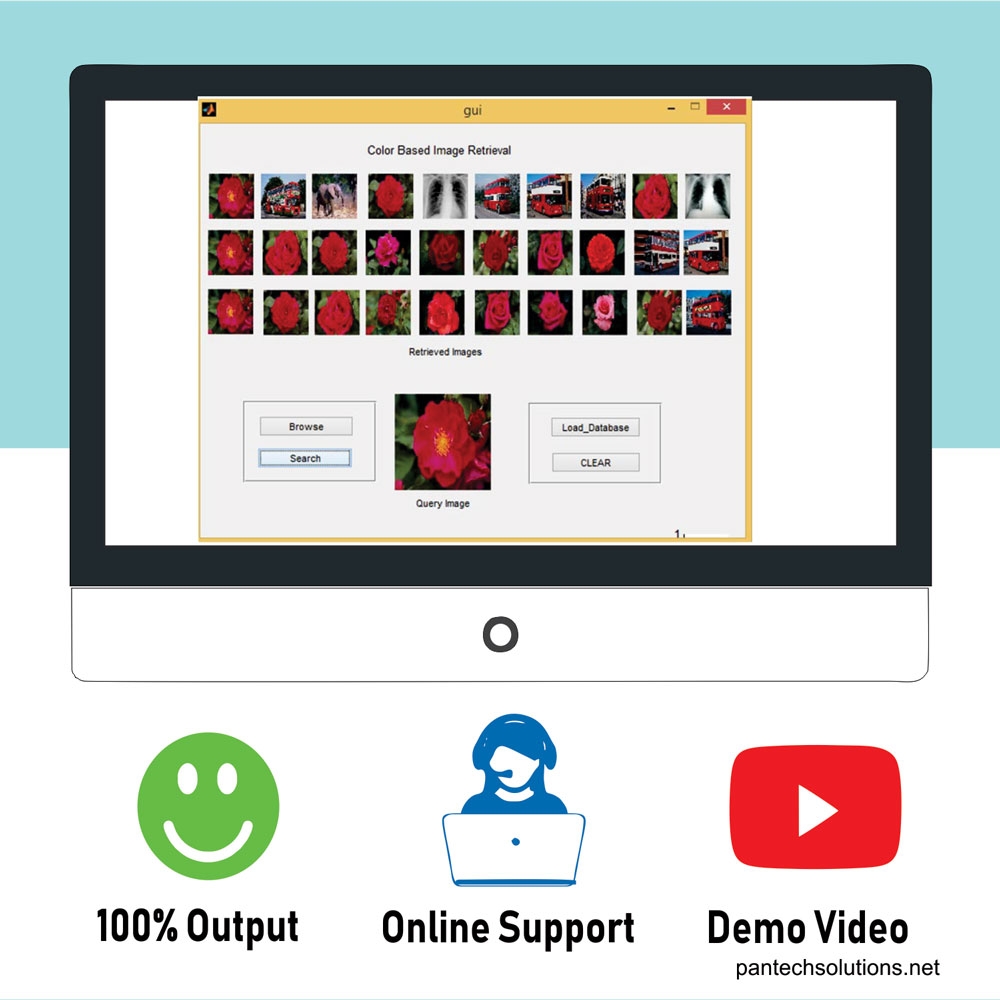
Image retrieval techniques are useful in many image-processing applications. Content-based image retrieval systems work with whole images and searching is based on comparison of the query. General techniques for image retrieval are color, texture and shape. These techniques are applied to get an image from the image database. They are not concerned with the various resolutions of the images, size and spatial color distribution. Hence all these methods are not appropriate to the art image retrieval. Moreover shape based retrievals are useful only in the limited domain. The content and metadata based system gives images using an effective image retrieval technique. Many other image retrieval systems use global features like color, shape and texture. But the prior results say there are too many false positives while using those global features to search for similar images. Hence we give the new view of image retrieval system using both content and metadata
EXISTING SYSTEM
This paper proposes a new simple method of DCT feature extraction that utilize to accelerate the speed and decrease storage needed in image retrieving process by the aim of direct content access and extraction from JPEG compressed domain. Our method extracts the average of some DCT block coefficients. This method needs only a vector of six coefficients per block over the whole image blocks. In our retrieval system, for simplicity, an image of both query and database are normalized and resized from the original database based on the cantered position of the eyes, the normalized image equally divided into non overlapping 8X8 block pixel Therefore, each of which are associated with a feature vector derived directly from discrete cosine transform DCT. Users can select any query as the main theme of the query image..
PROPOSED SYSTEM
Retrieval of Digital Images Using Texture Feature With Advanced Genetic Algorithm and DRLBP
This paper proposes an image retrieval method based on multi-feature similarity score fusion using genetic algorithm.
Content based image retrieval (CBIR) concerns the retrieval of similar images from image databases, using feature vectors extracted from images. These feature vectors globally define the visual content present in an image, defined by e.g., texture, colour, shape, and spatial relations between vectors. Herein, we propose the definition of feature vectors using the Local Binary Pattern (LBP) operator. A study was performed in order to determine the optimum LBP variant for the general definition of image feature vectors. The chosen LBP variant is then subsequently used to build an ultrasound image database, and a database with images obtained from Wireless Capsule Endoscopy. The image indexing process is optimized using data clustering techniques for images belonging to the same class.
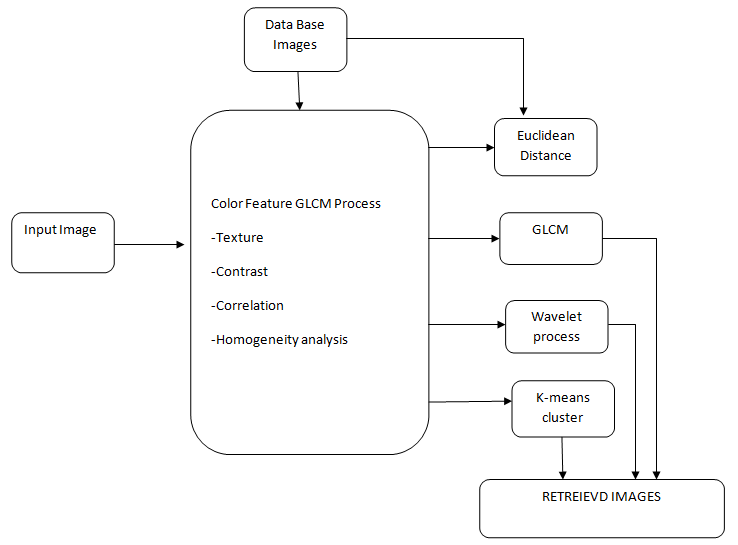
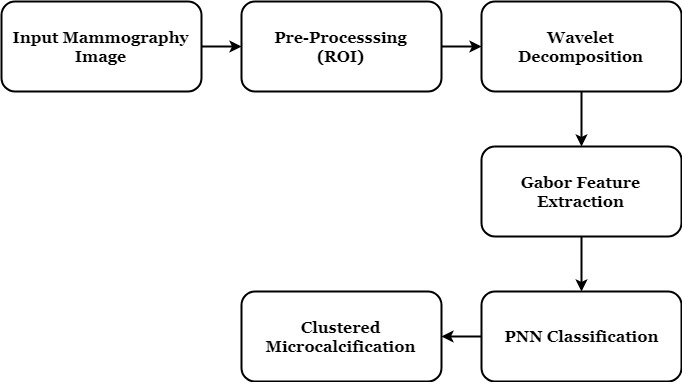
BLOCK DIAGRAM
ADVANTAGES
- No Data Loss
- Great Accuracy
APPLICATIONS
- Retrieving images
- Security analysis
- Tracking detection
SOFTWARE REQUIRMENT
- MATLAB 7.15 and above versions
MODULES
- GLCM
- DWT
- DRLBP
- K-means clustering
- NN
CONCLUSION
A novel architecture for a CBIR image database using a feature vector defined with a LBP operator and data mining techniques is proposed. Following this study, the most efficient way to globally represent the informational content present in an image is to define the feature vector using a circular LBP operator with radius 1 and 8 pixels neighborhood. Moreover, it is better to indirectly retrieve similar images from the databases using image models. This aspect significantly increases the accuracy of the retrieval process, and decreases the time for accessing information from the image database.
FUTURE ENHANCEMENT
- In future enhancements we extend our features selections and introduce other distance measures to the user in order to improve the results.
REFERENCES
[1] H. Lieberman, E. Rosenzweig, and P. Singh, Aria: An Agent for Annotating and Retrieving Images, Computer 34 (2001), 57–62.
[2] T. Kato, Database architecture for content-based image retrieval, Proceedings of SPIE – The International Society for Optical Engineering 16 (1992), 112-113.
[3] Y. A. Aslandogan and C. T. Yu, Techniques and Systems for Image and Video Retrieval, IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering 11(1999), 56–63.
[4] M. Peitkinen, A. Hadid, G. Zhao, and T. Ahonen, Computer Vision Using Local Binary Patterns, Computational Imaging and Vision 40 (2011), 13-47.
[5] C. Pavlopoulou, A. C. Kak and C. Brodley, “Content-based Image Retrieval for Medical Imagery” in Proceedings SPIE Medical Imaging: PACS and Integrated Medical Information Systems, San Diego CA, 2003.
[6] R. Weber, H. Schek, and S. Blott, A Quantitative Analysis and Performance Study for Similarity-Search Methods in High-Dimensional Spaces, Proceedings of 24rd International Conference on Very Large Data Bases (1998), 194–205.
[7] The CUReT database: http://www.cs.columbia.edu/CAVE/software/curet/html/about.php
[8] T, Ojala, M. Pietikäinen, and D. Harwood, A Comparative Study of Texture Measures with Classification Based on Feature Distributions, Pattern Recognition, 29 (1), (1996) 51-59
[9] L. Nannia, A. Lumini, and S. Brahnam, Local binary patterns variants as texture descriptors for medical image analysis, Artificial Intelligence in Medicine 49 (2010)
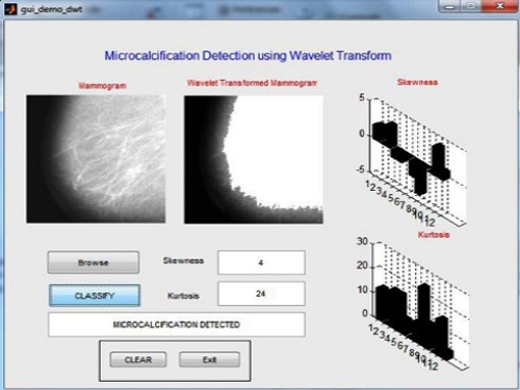
DEMO VIDEO


Reviews
There are no reviews yet.